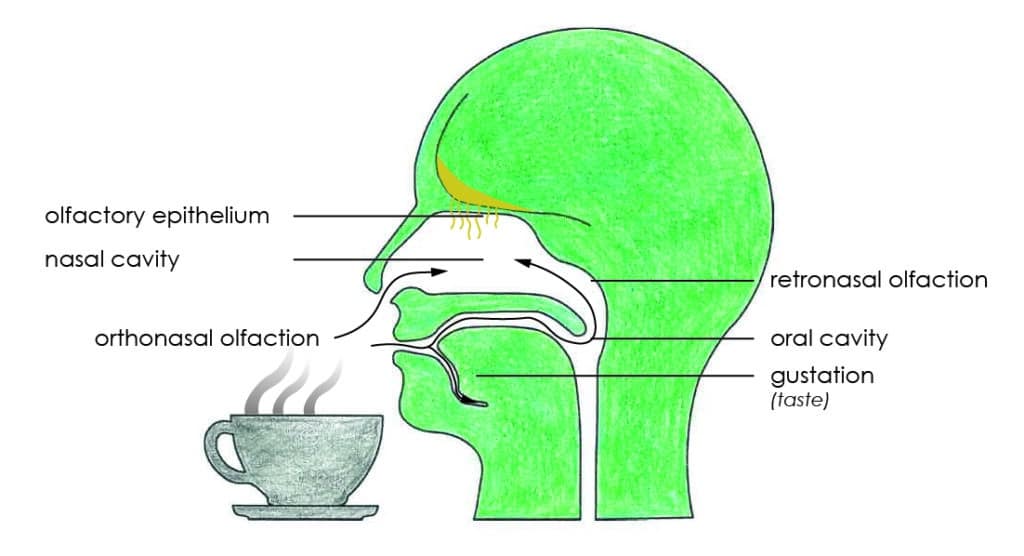
Taste and aroma work together to provide the full experience of any coffee. The taste are the sensations that we experience on our taste buds, while aromas are the sensations that we experience through Orthonasal olfaction to our nasal cavity, or retronasal, through our oral cavity and up to the olfactory epithelium.
Some believe that different taste buds are located on different regions of the tongue. But in reality, all taste buds on the tongue are capable of detecting all five primary tastes. However, certain regions of the tongue may be more sensitive to certain tastes than others. For example, the front of the tongue is generally more sensitive to sweet and salty flavors, while the back of the tongue is more sensitive to bitter flavors.
Taste can be classified into five basic categories: sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami. Aromas, on the other hand, can be classified into a wide range of categories, depending on the source of the aroma. Some common aroma categories include roasted, nutty, floral, fruity, and spicy. Both the taste and aromas play an important role in our enjoyment of our coffee, as well as in our perception of the world around us.
When we talk about the flavor of coffee, we talk about the perceived combination of taste, aroma and mouthfeel. Mouthfeel refers to the feeling in the mouth such as the texture, thickness, and creaminess, including the aftertaste.
Here is some of the key factors that contribute to the flavors and aromas of coffee:
1. Coffee Beans: The type of coffee bean used to make the coffee can have a significant impact on its flavor and aroma. Arabica beans are known for their mild, sweet flavor and aroma. Robusta beans, on the other hand, have a more robust, bitter flavor and aroma.
2. Roasting: The degree of roasting can also affect the flavor and aroma of the coffee. Lighter roasts tend to have a more acidic, fruity taste, while darker roasts tend to have a stronger, more bitter flavor.
3. Brew Method: Different brewing methods can also affect the flavor and aroma of coffee. For example, French press coffee is known for its bold, strong flavor, while pour-over coffee is known for its clean, crisp taste.
4. Additives: Adding cream, sugar, or other flavorings can also impact the flavor of the coffee. These additives can enhance or mask the natural flavors and aromas of the coffee.
5. Age: The age of the beans can also affect their flavor and aroma. Freshly roasted coffee beans tend to have a stronger, more complex flavor and aroma, while older beans can have a more stale, flat taste.
If you want to know more about what kind of taste and aroma you can find in a cup of coffee, then you can click here