Coffee berry or coffee cherry, also known as coffee fruit or cascara, refers to the fruit that surrounds the coffee bean. It is the outer layer of the coffee cherry. The coffee cherry is harvested from the coffee tree and has a complex anatomy. It is composed of several layers, each with a unique function. Here is a brief overview of the anatomy of the coffee bean:
Outer layer or seed coat (pericarp or exocarp): This is the layer that covers the entire bean and protects it from environmental damage. The layer is thin, tough, and often slightly sticky.
Pulp (mesocarp): Is a sweet, juicy and fleshy layer that contains sugars, acids, and other compounds that contribute to the flavor and aroma of the coffee.
Mucilage or Pectin : Is a sticky, gelatinous substance that surrounds the coffee beans inside the fruit of the coffee plant. It is a complex mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and other organic compounds, and it plays an important role in the development of coffee flavor and aroma. Pectin is found in the cell walls of many plants and is responsible for giving them structure and firmness.
Endocarp or parchment: This is a thin, paper-like, woody layer that surrounds the coffee bean inside the fruit of the coffee plant. It is the final layer that protects the coffee bean before it is harvested and processed for roasting. Endocarp is the layer that protects the bean during the drying process.
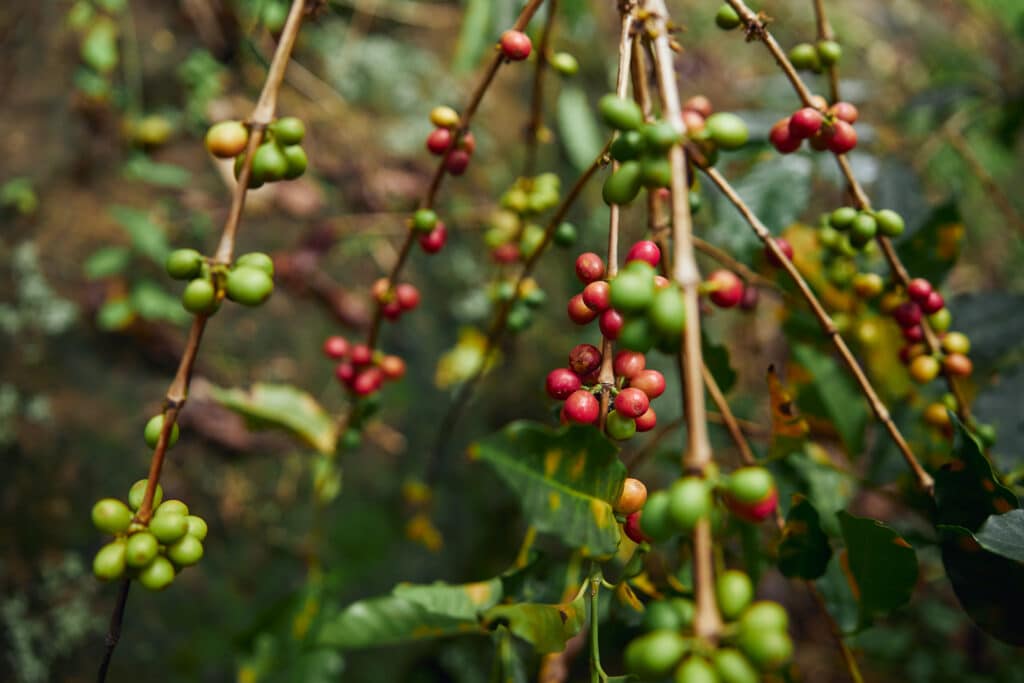

The layers, pulp, mucilage and endocarp is the outer layer that covers the coffee seed (or bean) and protects it from external damage. It is also known as the coffee cherry skin. The cherry skin, including the parchment layer, is the layer that is removed to reveal the green coffee bean, and to get it ready to the process of roasting
Silver skin (testa): This is a thin, papery layer that surrounds the green coffee bean. The layer is a silvery and translucent layer that is removed during the roasting process.
Bean (endosperm): This is the largest part of the coffee bean and contains the nutrients and energy that the coffee plant needs to grow. The endosperm is where the majority of the flavor and aroma compounds are stored. This part of the bean is also known as the “coffee meat.”
Bean (endosperm): This is the largest part of the coffee bean and contains the nutrients and energy that the coffee plant needs to grow. The endosperm is where the majority of the flavor and aroma compounds are stored. This part of the bean is also known as the “coffee meat.”
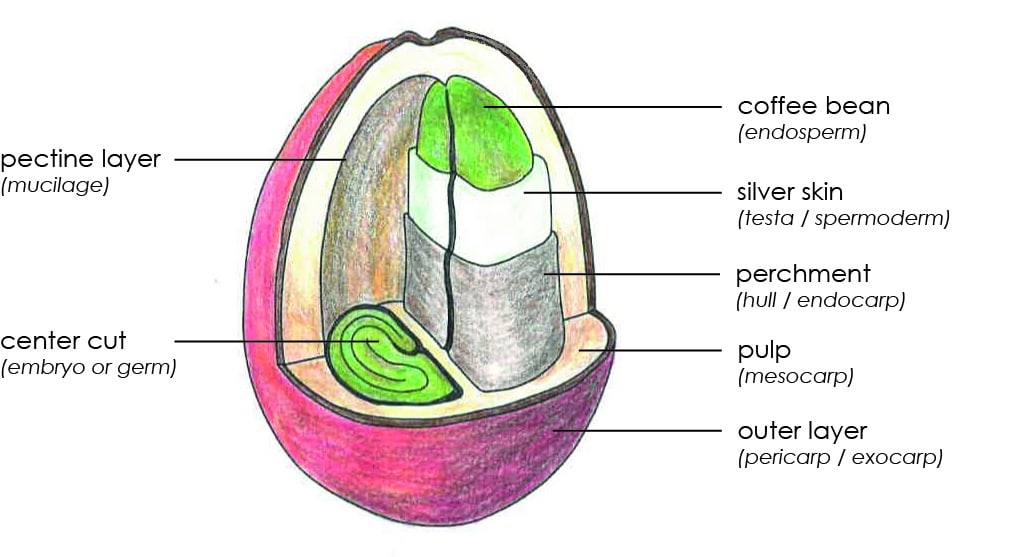
Center cut (Embryo or germ): This is the part of the coffee bean that will eventually sprout into a new coffee plant. During coffee processing, the embryo remains intact and is an essential part of the green coffee bean. When the coffee bean is roasted, the embryo is destroyed, as it cannot withstand the high temperatures of the roasting process.
Understanding the anatomy of the coffee bean is important for coffee growers, roasters, and baristas, as it can impact the flavor and quality of the coffee.